What Can Make Sciatica Worse? Top Factors & What to Avoid
What Can Make Sciatica Worse? This guide addresses how lifestyle choices, posture, and activities play a crucial role, offering insights for a mindful approach to alleviating sciatic discomfort.
Sciatica can be a debilitating condition, causing pain, numbness, or tingling that radiates from the lower back down to the legs. While many people experience relief through various treatments, certain activities and lifestyle choices can exacerbate the symptoms. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what can make sciatica worse and provide practical advice to help you manage and prevent increased discomfort.
Key Takeaways:
- Certain activities and habits can exacerbate sciatica symptoms.
- Maintaining proper posture and avoiding prolonged sitting are crucial for sciatica management.
- Understanding and avoiding specific triggers can help in reducing the frequency and intensity of sciatica flare-ups.
The Basics of Sciatica: A Quick Overview
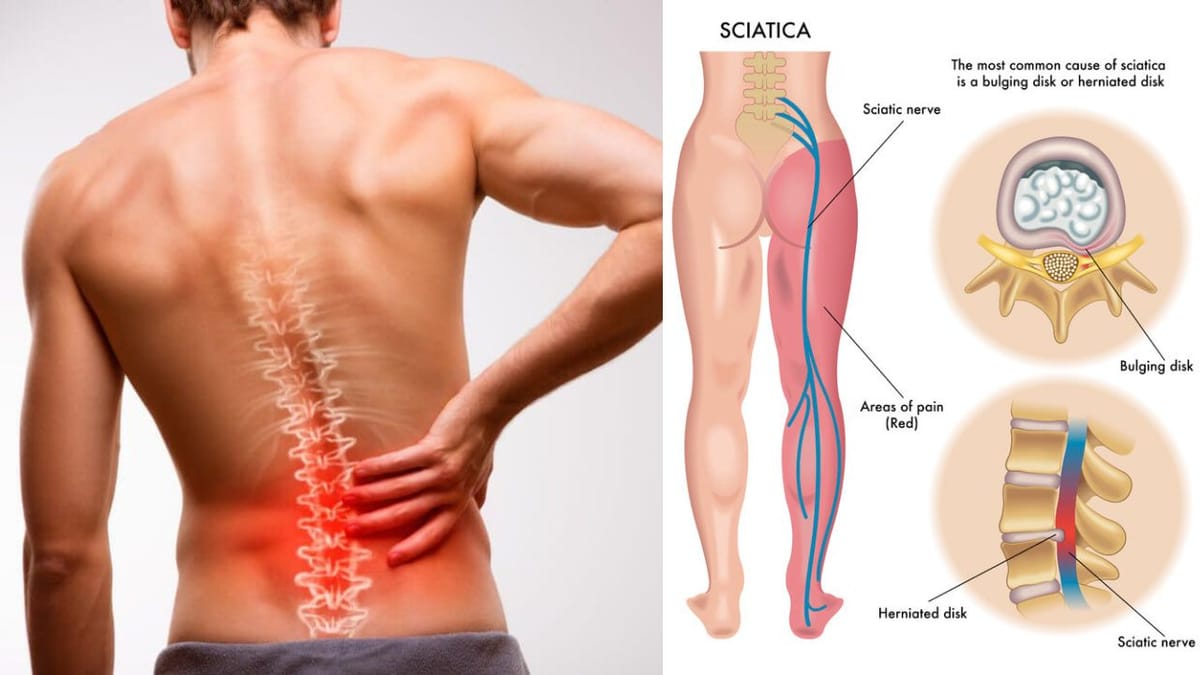
Sciatica is a term used to describe pain that travels along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. Typically, sciatica affects only one side of the body and can vary in intensity from a mild ache to a sharp, burning sensation or excruciating discomfort.
Recognizing Sciatica Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of sciatica is pain that radiates from your lower spine to your buttocks and down the back of your leg. This discomfort can be accompanied by sensations such as numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness along the nerve pathway. It's important to recognize these symptoms early to manage the condition effectively.
How Poor Posture Can Aggravate Sciatica
Poor posture is a significant contributor to worsening sciatica symptoms. Slouching or sitting incorrectly can put additional pressure on the spine and sciatic nerve. Maintaining a neutral spine position, especially when sitting for long periods, is essential to prevent additional strain on the nerve.
The Impact of Prolonged Sitting on Sciatica
Sitting for extended periods can cause the hip flexors to tighten and the lower back to become stiff. This can lead to increased pressure on the sciatic nerve. It's important to take regular breaks to stand and stretch, promoting circulation and reducing the risk of sciatica pain intensifying.
Excessive Weight as a Sciatica Aggravator
Carrying excess body weight, particularly around the midsection, can put additional stress on the spine and contribute to spinal changes that may irritate the sciatic nerve. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help alleviate this pressure and reduce sciatica symptoms.
The Role of High Heels in Sciatica Pain
Wearing high heels frequently can alter your posture and the alignment of your spine. This can lead to an increased risk of sciatica pain as the body compensates for the unnatural position of the feet and legs, which can put additional strain on the lower back and sciatic nerve.
How Stress and Tension Affect Sciatica
Stress and muscle tension can lead to tightness in the lower back muscles, which can exacerbate sciatica symptoms. Finding ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce muscle tension and alleviate sciatica pain.
The Connection Between Smoking and Sciatica
Smoking can impair blood flow and lead to degenerative changes in the spine, both of which can worsen sciatica symptoms. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for overall health but can also help reduce the severity of sciatica pain.
Inactivity & Weather
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to muscle weakness and decreased spinal support, which can make sciatica symptoms worse. Engaging in regular, low-impact exercise can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine and reduce the likelihood of sciatica pain flaring up.
Cold weather can cause muscles to tighten and become stiff, which may increase the discomfort associated with sciatica. Dressing warmly and using heat therapy can help keep muscles relaxed and reduce the impact of cold weather on sciatica symptoms.
Dehydration & Poor Sleeping Positions
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining the health of spinal discs and reducing the risk of disc herniation, a common cause of sciatica. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help keep discs hydrated and minimize the chances of a sciatica flare-up. A lack of sleep can cause muscle tightness and worsen sciatica symptoms.
Sleeping in positions that do not support the natural curve of the spine can lead to increased sciatica pain. Using a supportive mattress and pillow and sleeping in a position that maintains spinal alignment can help reduce the risk of worsening sciatica symptoms.
Understanding Sciatica and Pregnancy
Pregnancy can put additional strain on the spine and sciatic nerve due to the increased weight and changes in posture. Pregnant women should be mindful of their posture and engage in prenatal exercises to help manage sciatica symptoms.
The Role of Diabetes in Sciatica Symptoms
Diabetes can cause nerve damage, which may exacerbate sciatica symptoms. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help prevent nerve damage and reduce the severity of sciatica pain.
How Inadequate Exercise Can Worsen Sciatica
While excessive exercise can lead to injury and worsen sciatica, inadequate exercise can also be detrimental. A balanced exercise routine that includes stretching and strengthening can help maintain spinal health and prevent sciatica symptoms from worsening.
The Impact of Heavy Lifting on Sciatica
Improper lifting techniques can put undue stress on the spine and sciatic nerve. Learning and practicing proper lifting methods can help prevent sciatica pain from becoming more severe.
The Relationship Between Sciatica and Mental Health
Mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety can increase the perception of pain, including sciatica. Addressing mental health through therapy and medication can help improve pain management and reduce the impact of sciatica on daily life.
How Certain Medications Can Affect Sciatica
Some medications, particularly those that cause fluid retention or weight gain, can worsen sciatica symptoms. Discussing medication side effects with a healthcare provider can help identify alternatives that do not exacerbate sciatica pain.
The Dangers of Ignoring Sciatica Symptoms
Ignoring sciatica symptoms can lead to chronic pain and permanent nerve damage. Seeking medical attention early and following a treatment plan can help prevent symptoms from worsening.
The Importance of Ergonomics in Sciatica Prevention
An ergonomic workspace can help reduce the risk of sciatica by promoting proper posture and reducing strain on the lower back. Investing in an ergonomic chair and desk setup can be beneficial for those with sciatica.
How Nutrition Influences Sciatica Symptoms
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation that may irritate the sciatic nerve. Incorporating foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts into your diet can help manage sciatica symptoms.
The Benefits of Physical Therapy for Sciatica
Physical therapy can provide targeted exercises and stretches to help alleviate sciatica pain. A physical therapist can also offer guidance on how to avoid movements that may make sciatica worse.
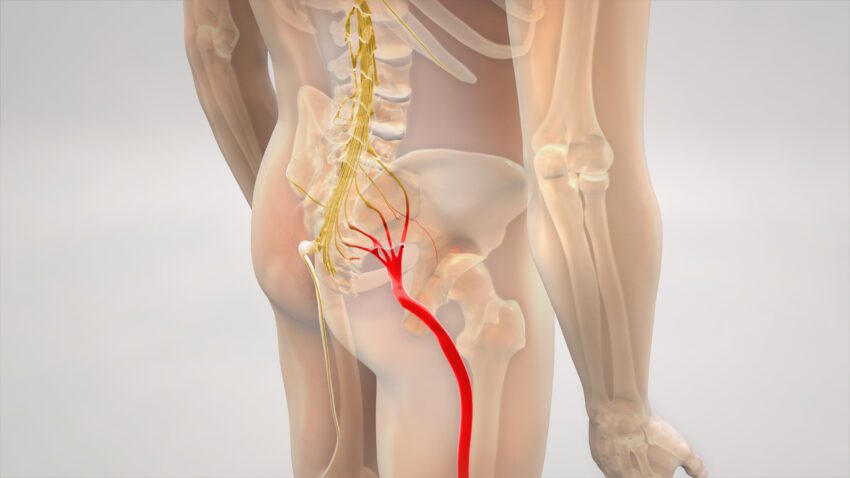
Sciatica and the Importance of Stretching
Regular stretching can help maintain flexibility and reduce tension in the muscles that may contribute to sciatica pain. Incorporating daily stretching routines, particularly for the lower back, hips, and hamstrings, can be beneficial for those with sciatica.
How to Manage Sciatica During Travel
Traveling can be challenging for individuals with sciatica due to prolonged sitting and carrying luggage. Planning to take frequent breaks and using supportive cushions can help manage sciatica symptoms during travel.
The Role of Alternative Therapies in Sciatica Management
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy can offer relief for some individuals with sciatica. Exploring these options with a healthcare provider can help determine the best approach for managing sciatica pain.
FAQ Section
Q: Can heavy lifting aggravate sciatica?
A: Heavy lifting can potentially aggravate sciatica, depending on various factors. Sciatica is often caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, and heavy lifting can contribute to this pressure in several ways.
- Increased Spinal Pressure: Lifting heavy weights, especially with improper form, can lead to increased pressure on the spine. This pressure may affect the intervertebral discs, potentially causing them to bulge or herniate and subsequently compress the sciatic nerve.
- Muscle Strain: Heavy lifting can strain the muscles surrounding the lower back, including those that interact with the sciatic nerve. This strain may exacerbate existing inflammation or irritation, contributing to sciatic pain.
- Poor Posture: Incorrect lifting techniques can lead to poor posture, placing additional stress on the lower back. This, in turn, may worsen the symptoms of sciatica by adding extra pressure to the nerve.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as lumbar disc issues, may be more susceptible to sciatica aggravation when engaging in heavy lifting activities. The added stress on the spine can exacerbate these underlying problems.
To minimize the risk of aggravating sciatica while lifting heavy, it's crucial to prioritize proper lifting techniques, maintain a strong core, and be mindful of one's physical limitations.
If someone is experiencing persistent sciatic pain or discomfort, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist for personalized guidance tailored to their specific condition. Always listen to your body and adjust your workout routine accordingly to prioritize long-term health and well-being.
Q: Does obesity contribute to sciatica?
A: Yes, obesity can indeed contribute to sciatica. Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, often caused by compression or irritation of the nerve roots in the lower spine. Obesity can contribute to sciatica in several ways:
- Increased Pressure on Spine: Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can add pressure to the spine. This extra load can compress the discs between the vertebrae, leading to conditions such as herniated discs that may contribute to sciatica.
- Inflammation and Nerve Compression: Obesity is associated with chronic inflammation. Inflammation can contribute to the compression of the sciatic nerve or the nerve roots, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness associated with sciatica.
- Poor Posture and Misalignment: Carrying excess weight can alter a person's posture, leading to misalignment of the spine. Poor posture and spinal misalignment can contribute to the compression of the sciatic nerve, exacerbating sciatica symptoms.
- Metabolic Factors: Obesity is often linked to metabolic conditions such as insulin resistance. These metabolic factors can contribute to inflammation and other physiological changes that may affect the nerves and increase the risk of sciatica.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Obesity is associated with a sedentary lifestyle, which can weaken the muscles that support the spine. Weak muscles may fail to adequately support the spine and contribute to conditions that lead to sciatica.
It's important to note that while obesity can be a contributing factor to sciatica, it is not the sole cause. Other factors such as age, genetics, and certain lifestyle choices also play a role. Addressing obesity through a combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications may help alleviate the impact on sciatica and improve overall spinal health. If you are experiencing sciatica or obesity-related health issues, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized advice and treatment.
Q: Is lack of exercise a factor in worsening sciatica?
A: The lack of exercise can indeed be a significant factor in worsening sciatica. Sciatica, characterized by pain along the sciatic nerve, often stems from compression or irritation of the nerve roots in the lower spine. Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining spinal health and preventing conditions that contribute to sciatica.
When we lead a sedentary lifestyle or lack regular physical activity, it can lead to weakened muscles, poor posture, and decreased flexibility—all of which contribute to increased pressure on the spine and the sciatic nerve. Exercise, particularly activities that strengthen the core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote overall spine health, can help alleviate sciatica symptoms.
Moreover, staying active helps in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing inflammation, and enhancing blood circulation—all essential factors in managing sciatic pain. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise regimen, as the type and intensity of exercises should be tailored to individual conditions and needs. Always prioritize gentle and low-impact activities, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, to support sciatica management effectively.
Q: Can stress worsen sciatica?
A: The stress can indeed exacerbate sciatica symptoms. Sciatica, often caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, can manifest as pain, tingling, or numbness radiating from the lower back down the leg. Stress contributes to this condition in several ways.
Firstly, stress can lead to muscle tension, especially in the lower back and pelvic area. When muscles surrounding the sciatic nerve become tight, it can increase pressure on the nerve, intensifying sciatic pain.
Secondly, stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone associated with the body's "fight or flight" response. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to inflammation, which may aggravate the already sensitive sciatic nerve.
Moreover, stress can negatively impact posture and body mechanics, potentially contributing to misalignments or increased pressure on the spine and nerves.
In conclusion, managing stress is crucial for individuals dealing with sciatica. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and regular exercise can not only promote overall well-being but also potentially alleviate the impact of stress on sciatica symptoms.
It's essential to address both the physical and mental aspects of sciatica for a comprehensive and effective approach to management.