What Aggravates Coccyx Pain? Common Triggers
Unmask the culprits behind that nagging coccyx pain and regain control of your comfort by avoiding prolonged sitting & seeking treatments.
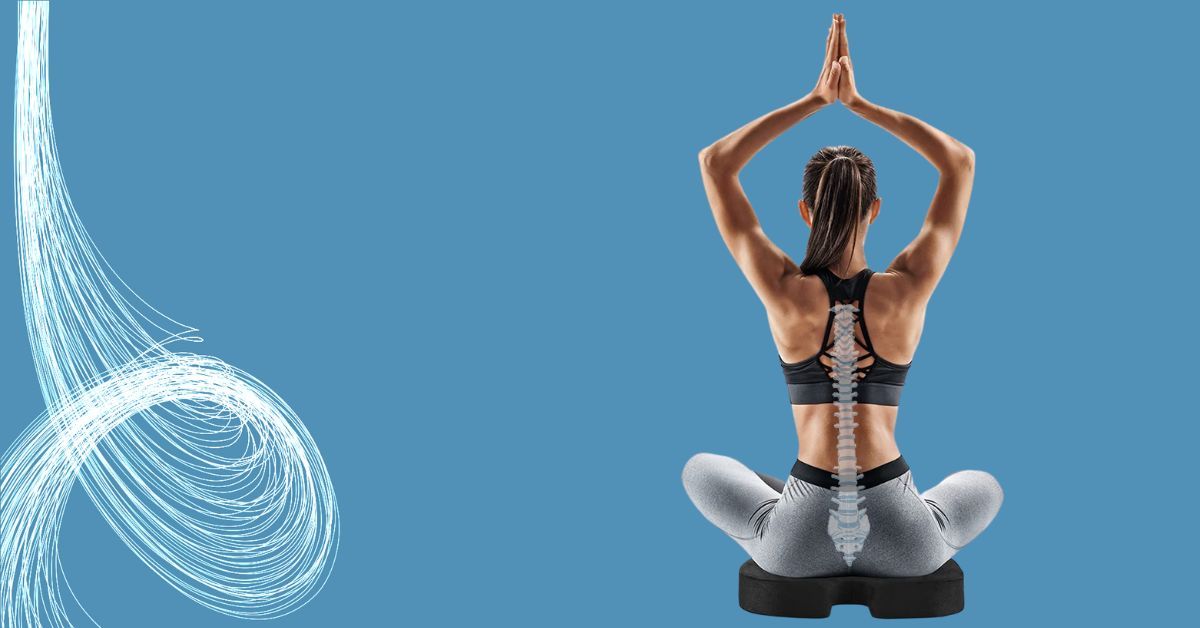

Well, you could say it's the world's most "behind"-the-scenes troublemaker. Picture this: You're at a family dinner, laughing at Uncle Joe's corny jokes when suddenly, your tailbone starts its stand-up routine – and it's no laughing matter. That's when you wonder, what did your coccyx ever do to deserve this agony?
In this article, we're peeling back the layers of the coccyx conundrum and revealing the culprits that make it throw its own, not-so-funny tantrum. So, what aggravates coccyx pain, you ask? The short answer: stay with us to uncover the not-so-comedic, but highly enlightening, truth. Your tailbone will thank you later.
Coccyx pain: What Causes It?
Coccyx pain, often referred to as coccydynia, can result from various causes and may be experienced as localized pain in the tailbone region. While the specific cause can vary from person to person, some common factors that contribute to coccyx pain include:
- Trauma: A common cause of coccyx pain is direct trauma, such as a fall onto the tailbone or a blow to the area. This can result in bruising, fractures, or dislocations.
- Childbirth: Women can experience coccyx pain following childbirth, particularly in cases involving difficult or prolonged labor where pressure on the tailbone is increased.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for extended periods on uncomfortable surfaces, can lead to coccyx pain due to increased pressure and strain on the tailbone.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repeated strain on the coccyx, such as cycling, rowing, or long hours of sitting at a desk, can contribute to chronic coccyx pain.
- Infections or Tumors: Although less common, infections or tumors in the coccyx area can cause pain and discomfort.
- Degenerative Conditions: Conditions like coccydynia, which involve inflammation or damage to the coccyx, can lead to chronic coccyx pain.
- Weight: Excess body weight can increase pressure on the tailbone when sitting, potentially leading to pain and discomfort.
- Bone Spurs: The development of bone spurs (bony projections) around the coccyx can cause irritation and pain. Congenital or acquired structural abnormalities of the coccyx can lead to pain in some individuals.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing the cause of coccyx pain, also known as coccydynia, typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Here's an overview of the diagnostic process:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will begin by asking you about your medical history, including details about the onset and duration of your coccyx pain, any recent injuries or traumas, and your general health.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination is conducted to assess the area of pain, identify any tenderness or deformities, and check for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests may be ordered, based on the doctor's recommendation, to further evaluate the coccyx and surrounding structures. Some common diagnoses include:
- X-rays for detailed images of the tailbone that can help identify fractures, dislocations, or structural abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans can offer a more comprehensive view of the coccyx and surrounding tissues, helping to detect issues such as infections, tumors, or disc-related problems.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography) may be recommended for a more detailed assessment of bony structures and fractures.
- Additional Tests: In some cases, additional tests or assessments may be required to rule out specific conditions or confirm a diagnosis. This may include blood tests to check for infections or inflammatory markers.
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): In certain situations, a digital rectal examination may be performed to evaluate the coccyx, rectum, and surrounding tissues for any abnormalities.
- Bone Scan: A bone scan may be recommended to assess the metabolic activity of the tailbone and surrounding bones, which can help identify conditions like infections or tumors.
- Consultation with Specialists: Depending on the diagnosis, your healthcare provider may refer you to specialists such as orthopedic surgeons, pain management specialists, or physical therapists for further evaluation and treatment.
Coccyx Pain Treatments/Remedies
The treatment of coccyx pain, also known as coccydynia, depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Here are some treatment options for coccyx pain:
Home Remedies/Measures
Coccyx Cushion or a donut cushion can help reduce pressure on the tailbone when sitting, providing comfort and relief. Check out our guide to find the best coccyx cushion.
Hot & Cold Therapy includes ice packs initially to reduce inflammation and then using warm compresses can help alleviate pain and relax muscles.
Sitz Baths Soaking in warm sitz baths can provide relief by relaxing the muscles around the coccyx and promoting circulation.
Activity that exacerbates pain and modifying sitting or exercise routines can help reduce coccyx pain.
Dietary Changes such as increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated, can alleviate pain associated with conditions like constipation or hemorrhoids.
Weight Management can reduce pressure on the lower back and coccyx, helping to alleviate pain.
Stress Management like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress, which can exacerbate pain.
Treatment/ Medication
Pain Medications include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation but should be used as directed.
Physical Therapy can provide tailored exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles around the coccyx, improve posture, and enhance mobility.
Injection Therapy In some cases, injections of corticosteroids into the affected area can help reduce inflammation and provide relief.
Chiropractic or osteopathic treatments may involve manual adjustments to the coccyx to reduce pain and improve alignment.
Ultrasound Therapy to promote healing and reduce pain in the coccyx area.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) therapy uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain by interrupting pain signals sent to the brain.
Medication Management for chronic or severe cases, prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants or nerve pain medications, may be considered.
Surgery
In severe cases of coccydynia that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options such as coccygectomy (removal of the coccyx) may be considered.
Key Takeaways!
Understanding the factors that aggravate coccyx pain is the first step toward finding relief. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes, making lifestyle adjustments, and exploring various treatment options, you can take a seat back in your life without the unwelcome discomfort. Remember, coccyx pain doesn't have to steal the spotlight – it's a challenge you can overcome, one step at a time.