How Do You Relieve Severe Coccyx Pain?
Coccyx pain and reclaim your comfort with these treatments, from the therapeutic embrace of coccyx cushions to the healing touch of physical therapy.
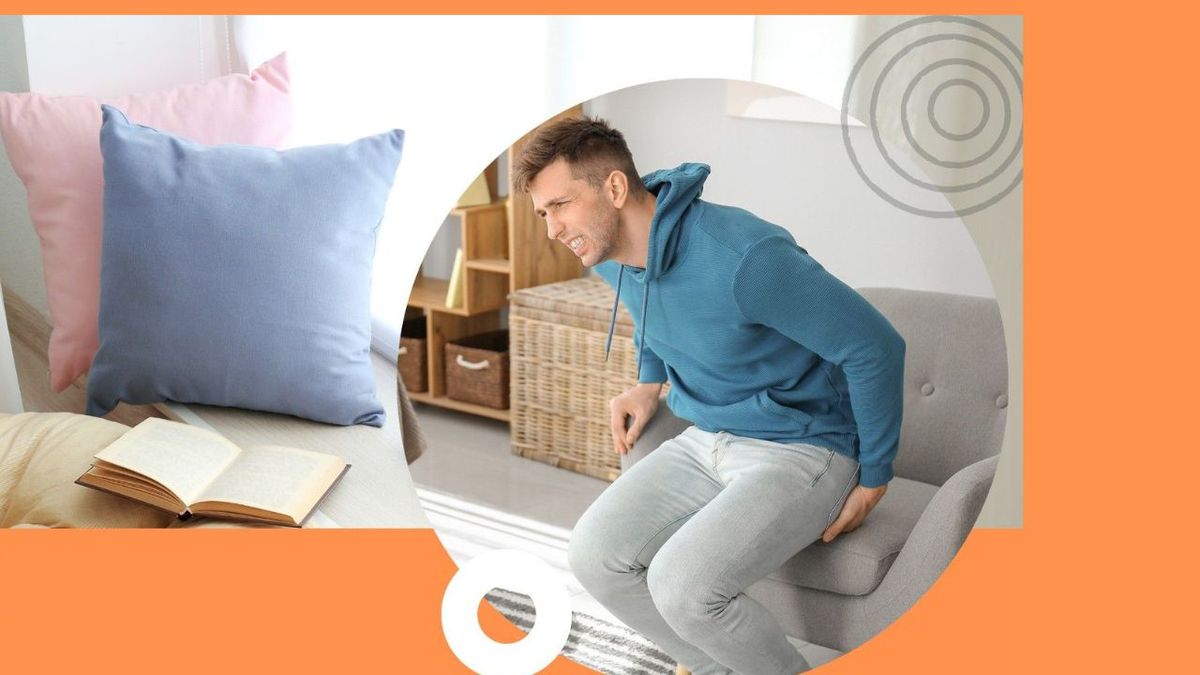

Tailbone pain is caused by repeated or prolonged strain on the coccyx – for example, after sitting for a long time while driving or cycling, by poor posture. Being overweight or underweight. Joint hypermobility (increased flexibility) of the joint that attaches the coccyx to the bottom of the spine.
But before you resort to drastic measures, allow us to introduce you to the secrets of coccyx comfort. In this article, we're going to pull back the curtain on how to vanquish severe coccyx pain and regain your throne as the King or Queen of the comfy chair.
So, how do you relieve severe coccyx pain, you ask? The short answer: stick around for the ultimate guide to a pain-free posterior paradise. Your tailbone will thank you later.
Self-Care Treatment for Coccyx Pain Relief
Relief from coccyx pain can be a welcomed reprieve, and self-care measures can play a pivotal role in achieving that comfort.
Here are some self-care treatments for coccyx pain relief:
- Coccyx Cushion: Invest in a quality coccyx cushion, also known as a donut cushion, which is designed to reduce pressure on your tailbone when sitting. Use it at home, in your car, or at the office to promote comfort. Focus on maintaining good posture when sitting.
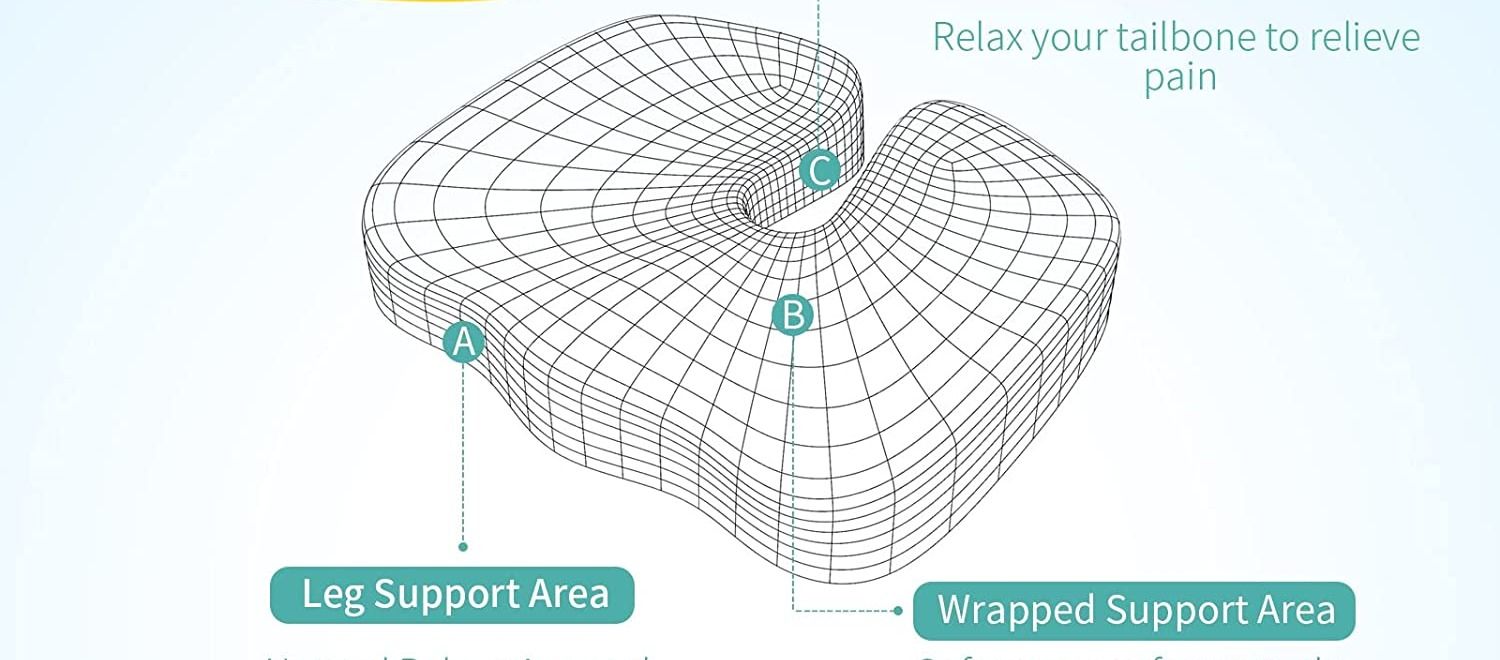
- Sit back in your chair, with your feet flat on the ground, and use a back support if needed to reduce pressure on the coccyx.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Apply a cold pack to the painful area in the initial stages to reduce inflammation and ease pain. After a couple of days, switch to a warm compress to relax muscles and stimulate blood flow.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort and reduce inflammation, but use them as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Tailbone Exercises: Gentle exercises can strengthen the muscles around the tailbone and improve stability. Pelvic tilts, gentle stretches, and Kegel exercises can be beneficial.
- Hot Baths: Soaking in a warm bath can provide relaxation and relief for coccyx pain. Consider adding Epsom salts to further ease muscle tension.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: If possible, take breaks from sitting for extended periods. Stand up, stretch, and walk around to alleviate pressure on the tailbone.
- Weight Management: If excess weight contributes to your coccyx pain, consider maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the lower back and tailbone.
- Hard Surfaces: Avoid sitting on hard, uncomfortable surfaces. Opt for a cushioned chair or use your coccyx cushion for added comfort.
- Hydration and Diet: Staying hydrated and maintaining a diet rich in fiber can help manage conditions like hemorrhoids, which may contribute to coccyx pain.
- Constipation & Stress: Constipation can lead to straining during bowel movements, potentially worsening coccyx pain. Make dietary and lifestyle changes to prevent constipation. Stress can exacerbate pain conditions. Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. They are widely available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription and are used for a variety of conditions, including arthritis, pain relief, and reducing fever. Here are some key points about NSAIDs:
Pain Relief: NSAIDs are effective in managing pain, whether it's mild to moderate pain from headaches, menstrual cramps, muscle aches, or more severe pain due to conditions like arthritis. Anti-inflammatory may help reduce inflammation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other inflammatory disorders.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs work by inhibiting enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) responsible for the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body that cause pain, fever, and inflammation.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Coccydynia
Coccydynia, a condition characterized by pain in the tailbone or coccyx, can often be managed and relieved with non-surgical treatments. These approaches can help alleviate pain and discomfort without the need for invasive procedures. Here are some non-surgical treatments for coccydynia:
- Coccyx Cushion: The use of a coccyx cushion, also known as a donut cushion, can significantly reduce pressure on the tailbone when sitting. This cushion is designed to promote comfort and relieve pain during activities that involve sitting.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on appropriate dosages and durations.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the painful area can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, offering relief. After a few days, switch to warm compresses to relax muscles and stimulate blood flow.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide tailored exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles around the coccyx, improve posture, and enhance mobility. Physical therapy can be particularly beneficial in chronic cases.
- Manual Manipulation: Chiropractic or osteopathic treatments can involve manual adjustments to the coccyx to reduce pain and improve alignment.
- Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to the area to reduce inflammation and provide relief. This is typically done under the guidance of a medical professional.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Therapeutic ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to promote healing and reduce pain in the coccyx area.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS therapy involves the use of low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain by interrupting pain signals sent to the brain.
- Dietary Changes: If constipation or hemorrhoids are contributing to coccyx pain, dietary adjustments, such as increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated, can help alleviate these conditions.
- Avoiding Prolonged Sitting: Take breaks and stand up regularly if you have a sedentary job or lifestyle to prevent putting prolonged pressure on the coccyx.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the lower back and coccyx, which can alleviate pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Stress and tension can exacerbate pain. Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Key Takeaways!
Relieving severe coccyx pain is not an insurmountable challenge. By implementing a combination of self-care techniques, from using coccyx cushions to maintaining good posture and exploring medical options when necessary, you can regain your comfort and quality of life. Remember, coccyx pain doesn't have to be a never-ending act of discomfort; it's a hurdle you can conquer, one cushion at a time.