Do Coccyx Cushions Really Work? Tailbone Relief Explained
Discover how coccyx cushions can alleviate tailbone pain, improve posture, and provide lasting comfort for extended sitting. Do they really work?

This question has left many of us skeptically eyeing our chairs like they're plotting a silent coup against our tailbones.
Here we're delving deep into the world of coccyx cushions, separating fact from fiction, and exploring whether these cushiony allies are more than just fluff. So, do coccyx cushions work? Well, the short answer is a resounding "Yes," but stick around to discover the science, stories, and secrets that make them your newfound sitting saviors.
What Is Your Coccyx?
The coccyx, often referred to as the tailbone, is the small bone at the base of the spine, just below the sacrum. The coccyx consists of three to five fused (joined) vertebrae and is an attachment point for several ligaments and muscles in the pelvic area.
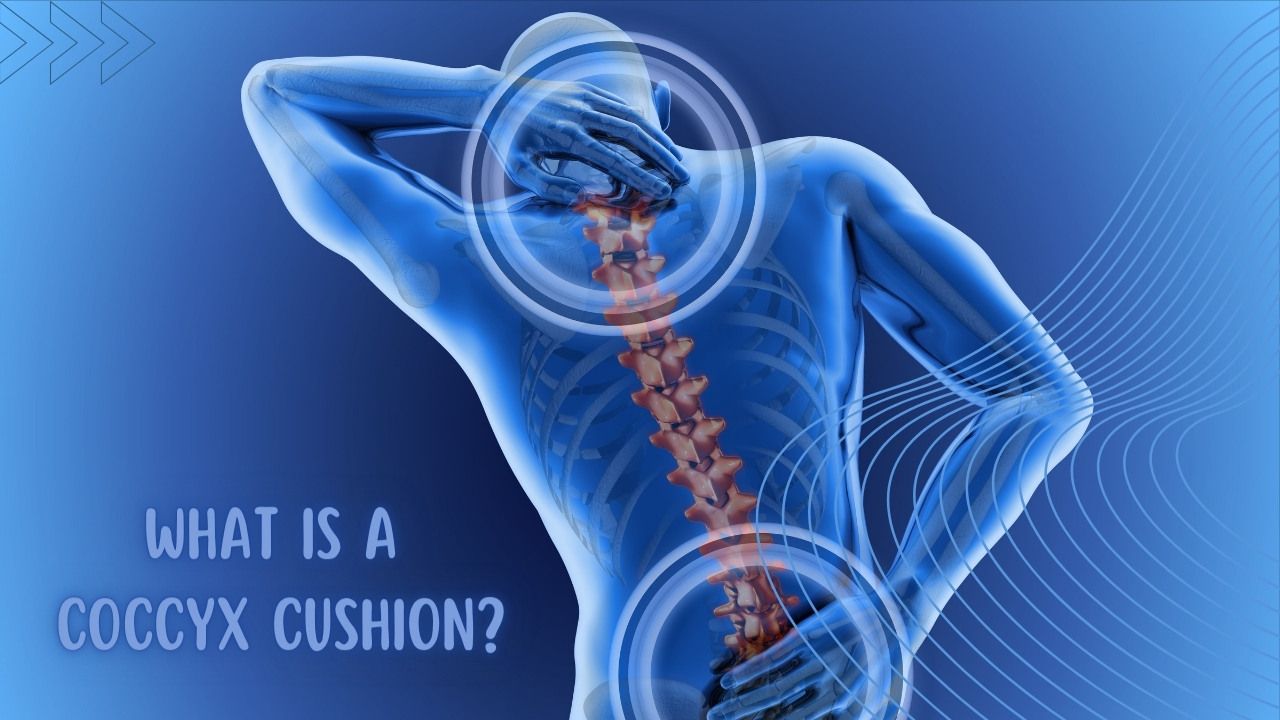
While the coccyx might seem small it plays a vital role in providing stability to the pelvis and supporting the muscles and ligaments surrounding it. Sometimes we experience discomfort or pain in the coccyx due to injury, strain, or medical conditions, and this is where coccyx cushions and specialized treatments come into play to provide relief.
Coccyx Injury Causes
Coccyx injuries can be quite painful and are often caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes of coccyx injuries include:
- Trauma that might be a direct blow or fall onto the tailbone is one of the most common causes of coccyx injuries. This can occur during activities like sports, slipping on ice, or falling down stairs.
- Childbirth can lead to coccyx injuries due to the pressure and movement during labor. This is more common in cases of prolonged or complicated deliveries.
- Prolonged sitting on hard surfaces, can lead to chronic irritation and inflammation of the coccyx. Occupations that require long hours of sitting may increase the risk.
- Excess body weight can put added pressure on the coccyx when sitting, potentially leading to injury or discomfort.
- In rare cases, infections or abscesses in the coccyx area can cause pain and discomfort.
- While uncommon, tumors or cysts in or near the coccyx can lead to discomfort and pain.
- Degenerative Conditions like coccydynia, which involve inflammation or damage to the coccyx, can cause chronic pain and discomfort.
What Is a Coccyx Cushion?
A coccyx cushion, also known as a tailbone cushion or a donut cushion, is a specially designed seat cushion created to provide relief and comfort for individuals who suffer from tailbone pain, coccyx injuries, hemorrhoids, or discomfort during prolonged periods of sitting.

The pillow typically features a U-shaped or wedge-shaped design with a central cutout or opening. This cutout or opening is strategically placed to alleviate pressure on the tailbone or coccyx, the small triangular bone at the base of the spine.
Coccyx cushions are made from various materials, including memory foam, gel-infused foam, or other supportive materials. The choice of material impacts factors like firmness, support, and heat retention. They also often come with removable and washable covers for easy maintenance.
The primary purpose of a coccyx cushion is to reduce the pressure and discomfort experienced while sitting, making it an ideal choice for those with tailbone injuries, post-surgery recovery, or conditions like hemorrhoids. These cushions can be used on a variety of seating surfaces, including office chairs, car seats, wheelchairs, and more, providing relief and improving overall comfort during sitting.
Preventing Coccyx Injuries
Preventing coccyx injuries, or tailbone injuries, is essential for maintaining comfort and avoiding pain in the lower spine. While some accidents are unforeseeable, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of coccyx injuries:
Maintaining good posture while sitting is crucial. Sit back in your chair with your feet flat on the ground and your weight evenly distributed. Proper posture can help prevent undue pressure on the coccyx.
If you spend extended periods sitting, check your posture and get some supportive device using a coccyx cushion or a donut cushion. These can help reduce pressure on the tailbone, especially if you have a sedentary job.
Strengthen core muscles can help support your spine and provide stability. Regular exercise can help prevent injuries and pain in the lower back and tailbone area. If you participate in sports or activities that involve a risk of falling, such as cycling, skiing, or skating, always wear protective gear. Helmets, padding, and safe techniques can reduce the risk of coccyx injuries.
For women giving birth, working with healthcare professionals to ensure proper birthing techniques can reduce the risk of coccyx injury during childbirth. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the stress on the tailbone and lower back, decreasing the risk of injury.
If your job or lifestyle requires long periods of sitting, take frequent breaks to stand, walk, or stretch. This helps alleviate pressure on the tailbone.
Use ergonomically designed chairs and seating to promote proper posture and reduce pressure on the coccyx. If you experience persistent pain in the coccyx area or suspect an injury, consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent further complications.
Who Needs a Coccyx Cushion?
If you have a coccyx injury condition, you may benefit from using a coccyx cushion. Anyone suffering from coccyx pain or coccyx injuries, such as fractures, dislocations, or bruising, can find relief through the use of coccyx cushions. These cushions help reduce pressure on the injured area and promote faster healing.
- Hemorrhoid Sufferers: Coccyx cushions are often recommended for people dealing with hemorrhoids. The cushion's central cutout minimizes pressure on the rectal area, providing comfort during sitting and potentially reducing irritation.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: After surgeries involving the tailbone or the surrounding areas, coccyx cushions can offer relief and comfort during the recovery process, helping patients avoid post-operative discomfort.
- Pregnant Women: Many pregnant women experience tailbone pain due to the increased pressure on the coccyx during pregnancy. Coccyx cushions can alleviate this discomfort and make sitting more bearable.
- Office Workers: Individuals with desk jobs or who spend extended hours sitting at a computer can benefit from coccyx cushions. These cushions improve posture and reduce pressure on the tailbone, reducing the risk of chronic lower back pain.
- Wheelchair Users: People who use wheelchairs for mobility may experience pressure sores, discomfort, or pain due to prolonged sitting. Coccyx cushions can help distribute the pressure more evenly and enhance comfort.
- Long-Distance Drivers: Truck drivers or individuals who frequently embark on long road trips can use coccyx cushions to make their journey more comfortable by reducing the pressure on the tailbone during extended periods of sitting.
- Seniors: Older adults may experience age-related pain or discomfort in the lower back and coccyx. Coccyx cushions can help them maintain better comfort and posture when sitting.
- Athletes: Athletes recovering from injuries or experiencing muscle soreness can benefit from coccyx cushions to alleviate pressure on sensitive areas during rest and recovery periods.
- Individuals with Sciatica: People dealing with sciatica, a condition that can cause radiating pain along the sciatic nerve, may find coccyx cushions helpful in reducing pressure on the lower spine.
Usage
- Coccyx Pain or Injury: If you have pain or an injury in your tailbone area, a coccyx cushion can help alleviate discomfort by reducing pressure on the injured or sensitive region.
- Hemorrhoids: People with hemorrhoids often experience pain or discomfort when sitting. The central cutout in a coccyx cushion can help relieve pressure on the rectal area, making sitting more bearable.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: After surgeries that involve the tailbone or the surrounding areas, such as pilonidal cyst removal or coccygectomy, a coccyx cushion can provide comfort and support during the recovery period.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women frequently experience tailbone pain due to increased pressure on the coccyx. Coccyx cushions can help reduce this discomfort and make sitting more comfortable.
- Chronic Lower Back Pain: If you suffer from chronic lower back pain or discomfort, a coccyx cushion can improve your posture and reduce pressure on the tailbone, potentially providing relief.
- Office Work: Individuals with desk jobs or who spend extended hours sitting at a computer can benefit from coccyx cushions. They promote better posture and minimize pressure on the tailbone, reducing the risk of developing chronic lower back pain.
- Wheelchair Use: People who rely on wheelchairs for mobility may experience discomfort or pressure sores from prolonged sitting. Coccyx cushions can help distribute the pressure more evenly and enhance comfort.
- Long-Distance Travel: Long drives or flights can be uncomfortable, especially for the tailbone. Coccyx cushions make sitting for extended periods more bearable and reduce the risk of discomfort.
- Athletic Recovery: Athletes recovering from injuries or experiencing muscle soreness can use coccyx cushions during rest and recovery periods to alleviate pressure on sensitive areas.
- Sciatica: If you suffer from sciatica, a condition that can cause radiating pain along the sciatic nerve, a coccyx cushion can help reduce pressure on the lower spine, offering relief during seated activities.
Key Takeaways!
Coccyx cushions undeniably work, providing relief from tailbone pain, improving posture, and enhancing overall comfort. Their versatility makes them invaluable tools in various scenarios, from post-surgery recovery to everyday seating, ensuring that your sitting experience is both pain-free and comfortable. So, if you've ever questioned the efficacy of coccyx cushions, rest assured that they are more than mere seat savers – they're your ticket to a more comfortable and pain-free seated life.